- Osmosis is a specialized diffusion resulting from the presence of a semi-permeable membrane
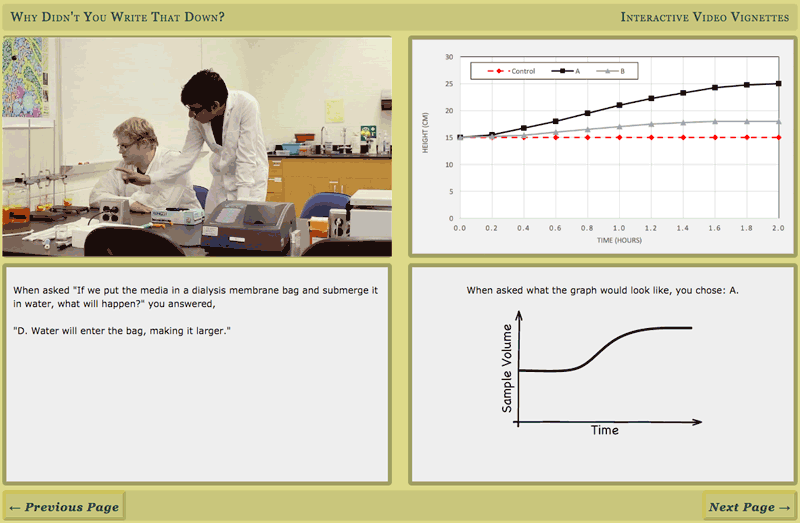
- Make a line graph demonstrating the change in volume over time due to osmosis
- Correctly predict the direction of solute and solvent movement across a semi-permeable membrane
- Explain that molecular motion is random, but overall movement goes in a particular direction due to entropy
- Explain that motion is continual in all directions, before and after equilibrium is reached
- Correlate concept of osmosis to biological function (such as transpiration, kidney function)
- Problem-solving in the lab: Constructing a hypothesis and testing it by setting up an experiment, collecting data, graphing it, and analyzing the graph to draw conclusions.
Vision and Change Core Concepts and Competencies (http://visionandchange.org)
Core Concept:
Structure and Function: Basic units of structure define the function of all living things.
Core Competencies:
Ability to apply process of science: Biology is evidence based and grounded in the formal practices of observation, experimentation, and hypothesis testing.
Biocore Guide (Brownell et al., https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.13-12-0233)
Structure and Function: The structure of a cell--its shape, membrane, organelles, cytoskeleton, and polarity--impacts its function.
Process of Science Skills, Pelaez, N, et al. “The Basic Competencies of Biological Experimentation: Concept-Skill Statements“ (2017). PIBERG Instructional Innovation Materials. Paper 4. http://docs.lib.purdue.edu/pibergiim/4
Hypothesis generation & testing
Identification of proper controls
Comparison requires holding all but the queried variable constant
Transfer of knowledge from other subjects/classes
Visual representations used for interpretation of data
- Copy the URL to the Clipboard. Either paste it into an email to your students, or use it to create a link in your course management system.
- Solute rather than water is the basis of osmosis
- Failure to recognize water as having relative concentration
- Sugar concentration could be measured with a spectrophotometer
- A solution can be separated by centrifugation
- Sugar changes the pH of a solution
- Water moves because it is attracted to the solute
- Osmosis is movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane
- Osmosis is a form of diffusion, which means a substance moving down its concentration gradient (in this case of water, not solute)
- Osmosis can be observed using a dialysis membrane, which allows passage of water but not solute: volume will increase on the higher solute concentration side (lower relative water concentration side) as water moves in
- A solute cannot be separated from its solvent by centrifugation
- Sugar does not affect the pH of an aqueous solution
- Sugar does not absorb light (cannot be detected with a spectrophotometer)
- Water can be represented as particles (molecules) that have concentration
Exploratorium Teacher Institute. Naked Egg. https://www.exploratorium.edu/snacks/naked-egg
El Paso Community College Biology at Transmountain, Diffusion and Osmosis lab, http://www.epcc.edu/Biology/Documents/Diffusion_and_Osmosis/Osmosis_and_Diffusion_Lab.pdf
Transpiration- Water Movement through plants – Introduction. Interactive Animation. http://croptechnology.unl.edu/pages/informationmodule.php?%20idinformationmodule=1092853841&topicorder=2&maxto=8&minto=1
- PDF (Adobe Acrobat) format: Click here to download
Acknowledgement
This material is based in part upon work supported by National Science Foundation (NSF) grants 1432286 and 1432303. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Ó2018, RIT. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.